Thermal cameras have emerged as vital tools across various industries. They detect infrared radiation, converting it into thermal images. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the global thermal camera market is projected to reach $5.8 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing demand in sectors like surveillance, firefighting, and automotive.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in thermal imaging technology, states, “Thermal cameras provide insights beyond visible light. They reveal temperature differences that are critical for safety.” These insights help in identifying heat loss in buildings or spotting malfunctions in machinery. However, the technology isn't perfect. Misinterpretations can occur, especially in complex environments.
As we explore thermal cameras, it’s essential to acknowledge the limitations. Shadows and reflective surfaces can skew results. Users must learn to interpret data correctly to avoid errors. Understanding these nuances helps harness the full potential of thermal cameras in day-to-day applications.
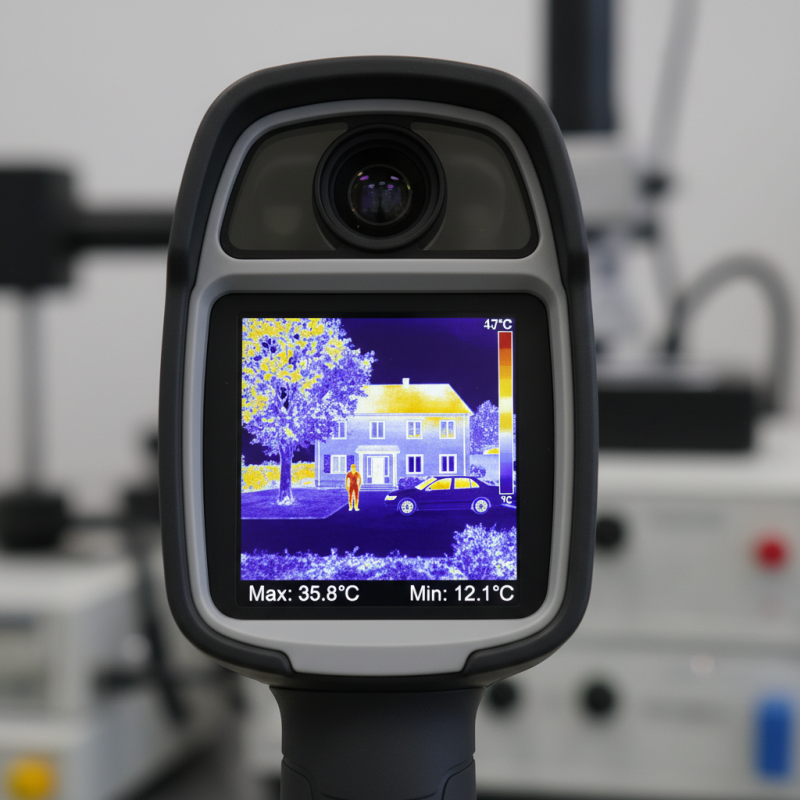

A thermal camera is a device that detects infrared radiation. It converts this radiation into an image. This technology enables us to see heat. Unlike regular cameras, thermal cameras can work in total darkness. They reveal temperature differences in objects and environments.
These cameras are used in various fields. For instance, they assist in building inspections by identifying heat loss areas. Firefighters use them to locate hotspots in smoke-filled environments. In wildlife studies, they help track animals without disturbing them. However, these applications can have challenges. Sometimes, thermal images can be misinterpreted. Different materials might emit heat distinctly, leading to confusion.
Users must also maintain the equipment properly. A dirty lens can compromise image quality. Regular calibration is necessary to ensure accurate readings. Understanding how to interpret thermal images takes practice. Training is essential to avoid overlooking critical details. Despite these challenges, thermal cameras offer valuable insights into our world. They bridge the gap between the visible and the invisible.
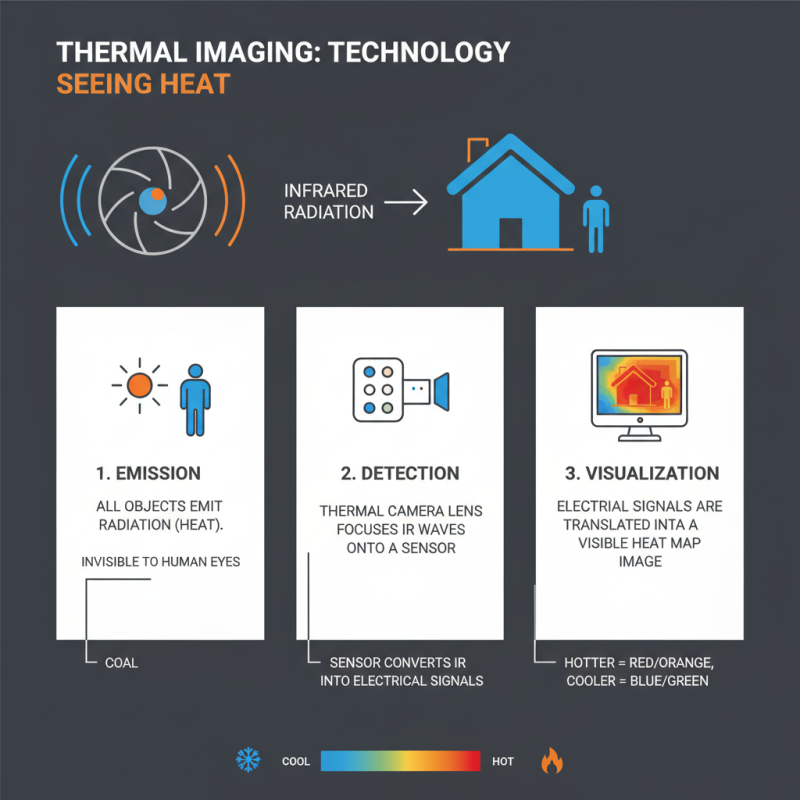
Thermal imaging technology captures heat emitted by objects. This process allows us to visualize temperature differences. At its core, thermal cameras detect infrared radiation. Human eyes cannot see this light, but thermal sensors can convert it into visible images.
In various industries, thermal imaging is invaluable. For example, the building inspection sector reports that 90% of energy leaks occur due to insulation failures. Detecting these leaks early can save significant energy costs. Additionally, in the healthcare industry, it plays a role in identifying fevers. A study indicates that thermal cameras could identify 95% of elevated body temperatures, enhancing public health monitoring.
Challenges remain in the field. Thermal cameras can be affected by environmental factors such as humidity and wind. In outdoor settings, their accuracy may decrease. Adjusting for these factors is crucial to obtain reliable data. Despite advancements, operators need to remain cautious and continuously update their skills. Staying informed can improve the effectiveness of thermal imaging applications across various fields.
Thermal cameras are intricate devices designed to visualize heat radiation. Understanding their components is crucial for effective usage. The core part of a thermal camera is the sensor. It detects infrared radiation emitted by objects. This sensor converts thermal energy into an electrical signal. Such signals form the basis of thermal images.
Another key element is the lens. Unlike typical camera lenses, thermal lenses are crafted from materials like germanium or chalcogenide glass. They ensure accurate focus on heat signatures. The camera also incorporates a display system. This displays the thermal image in real-time, allowing users to interpret data quickly. The processing unit is where signal conversion takes place. It turns raw data into a format users can understand.
Understanding these components helps users grasp thermal cameras' capabilities. Each part plays a fundamental role. A failure in any segment can lead to misinformation. Clear awareness of how they work can enhance operational efficiency, yet not everyone fully grasps these technologies. This gap can often result in misinterpretations of thermal imagery. Hence, reflection on one’s understanding and application of thermal cameras is essential.
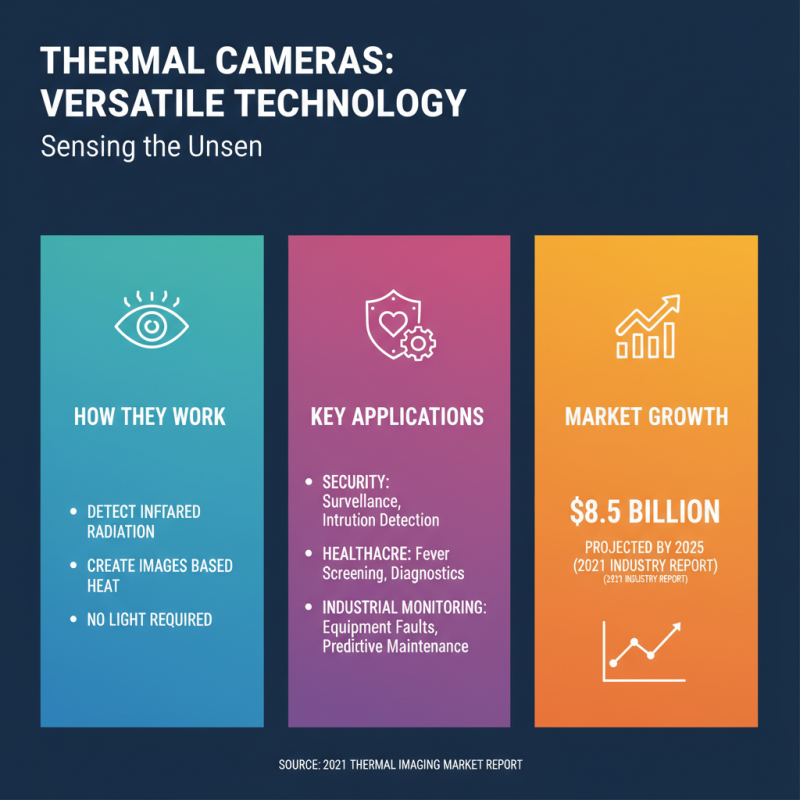
Thermal cameras are versatile tools used across various fields. Their ability to detect infrared radiation enables applications in security, healthcare, and industrial monitoring. According to a 2021 industry report, the thermal imaging market is projected to reach $8.5 billion by 2025, demonstrating growing interest and reliance on this technology.
In security, thermal cameras enhance surveillance capabilities. They work effectively in low-light conditions. A study found that such cameras can improve surveillance effectiveness by over 40%. However, they are not foolproof. False alarms can occur, as they may detect temperature variations from non-threatening sources, like animals.
In healthcare, thermal imaging is used for detecting fevers and other medical conditions. Research indicates a significant reduction in patient wait times. Yet, reliance solely on thermal cameras in diagnostics is questioned. They should be part of a broader strategy, as they may miss some medical issues. Balancing their use with traditional methods remains essential for accuracy.
Thermal cameras detect heat. They translate infrared radiation into images.
This makes it easy to see temperature differences.
Calibration ensures accuracy in readings. Without proper calibration, users may misinterpret the data.
Measurements from thermal cameras require understanding. They can show temperature ranges. However, external factors can affect these readings.
For example, reflective surfaces might distort images. Shadows can also complicate interpretations. Users must be aware of these pitfalls.
Calibration is essential for reliable results. Regular checks against known temperature sources help maintain accuracy.
Sometimes, issues arise from faulty equipment or improper settings. Continuous learning about thermal technology enhances the effectiveness of these devices.
It is a journey, not a destination. Users must reflect on their practices and adjust accordingly.